Chart 1: Key actors in public cultural policy making
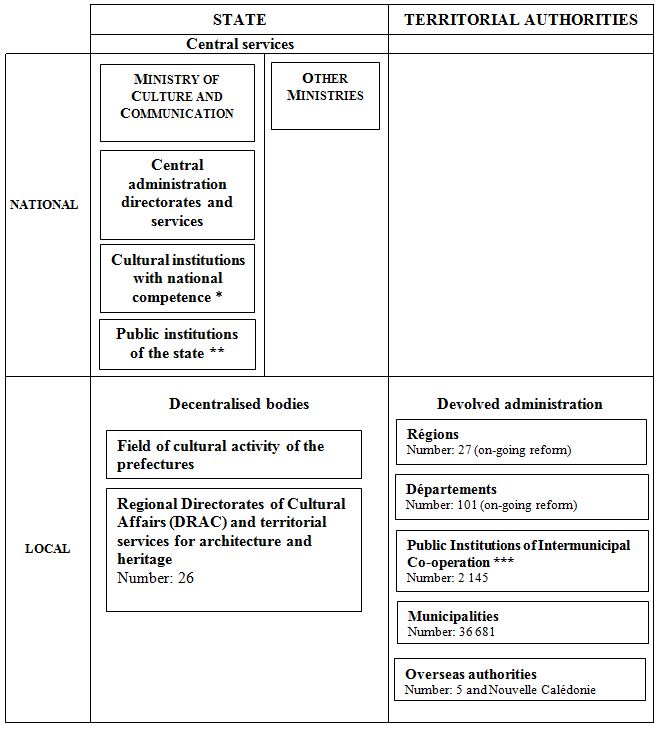
Sources : Ministry of Culture website (http://www.culturecommunication.gouv.fr) ; Les collectivités locales en chiffres 2016 (http://www.collectivites-locales.gouv.fr)
* Cultural institutions with national competence (27 in 2016, including 16 national museums): institutions directly attached to the central administration of the Ministry of Culture and Communication. They have functions in the field of management, technical studies, formation, and activities of production of goods or provision of cultural services in national matters. Examples: national archives, research and restoration centres, museums, media libraries and national libraries of architecture and heritage, etc…(complete list on the Ministry website)
** Public institutions of the State (76 in 2016): cultural organisations under the supervision of the State, having their own legal status, as well as administrative and financial autonomy e.g.: national museums, national arts centres, national academies, national art schools, etc… Ex. : Centre national d’art et de culture Georges Pompidou, Académie de France à Rome, Centre des monuments nationaux, Centre national de la cinématographie et de l’image animée, national music academies, national schools of art and architecture (20)…
*** Public Institutions of Inter-municipal Co-operation (EPCI): groupings of municipalities which aim to develop joint projects in various fields. The EPCI’s are subjected to common, homogeneous and comparable rules with those of the territorial authorities e.g.: the communautés de communes, the communautés d’agglomération, the communautés urbaines, syndicats intercommunaux, métropoles since 2015
Chart 2: Ministry of Culture and Communication: central directorates and divisions in 2016 (upload it in http://traduction.culture.gouv.fr/url/Result.aspx?to=en&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.culture.gouv.fr%2FNous-connaitre%2FOrganisation)
In the framework of the national programme of revision of public policies (Révision générale des politiques publiques), the organisational chart of the Ministry was reorganised in 2010 in four general directorates:
- a General Secretariat, which assists the Minister in all the general administrative matters and coordinates crosscutting cultural policies;
- a General Directorate of Heritage, constituted from the former Directorate of Museums (DMF), the Directorate of Architecture and Heritage (DAPA) and the Directorate of Archives (DAF);
- a General Directorate of Artistic Creation, which gathers the former Directorate of Music, Dance, Theatre and Performing Arts (DMDTS) and Visual Arts Division (DAP); and
- a General Directorate of Media and Cultural Industries that defines, coordinates and evaluates the State policy concerning media pluralism and cultural economy (advertising, broadcasting, music and publishing industry), and all the services of digital communication to the public. This Directorate supervises the National Centre of Cinema and Animation (Centre national du cinéma et de l’image animée).
In addition:
- the General Delegation (Division) of the French Language and Other Languages of France (DGLFLF);
- the Minister’s cabinet formed by technical councillors;
- special ministerial departments and bodies: Committee for the History of the Ministry of Culture and many other advisory commissions (see chapter 1.2.5), including some advisory High Councils: Haut Conseil de l’éducation artistique et culturelle, Conseil national de la culture scientifique, technique et industrielle, Conseil supérieur de la propriété littéraire et artistique;
- the General Inspectorate of Cultural Affairs;
- a State Senior Official for Security and Defence;
- a State Senior Official for Promotion of Equality between men and women
- a State Senior Official for Diversity
- a State Senior Official for Sustainable Development
- regional offices representing the government at the local level (comprising 13 mainland Regional Directorates and 7 bureaus in overseas territories), which implement national policies adapted to the regional context (including overseas territories), and also include special departments to deal with urbanism, architecture and heritage: the Services territoriaux de l’architecture et du patrimoine;
- public bodies (76 in 2016): institutions to which the State has accorded a specific legal status and financial autonomy; public bodies are State-supervised legal entities under public law; and
- institutions under national jurisdiction (27 in 2016) including numerous national museums).

Comments are closed.