7. Financing and support
Lithuania
Last update: May, 2022
In 2020, Lithuania's GDP at current prices was 49 507 million EUR; GDP per capita at current prices was 17 710 EUR. Total general government expenditure was 21 233.8 million EUR. Public expenditure on recreation, culture and religion* at all levels of government was 701.9 million EUR. The central government’s share of expenditure was 360.4 million EUR, and the share of local governments was 341.5 million EUR. Public expenditure on recreation, culture and religion in percentage of the total public expenditure was 3.3 %, and in percentage of GDP was 1.4 %. Public expenditure on recreation, culture and religion per capita was 250 EUR.
Figure 4. General government expenditure in Lithuania in 2020
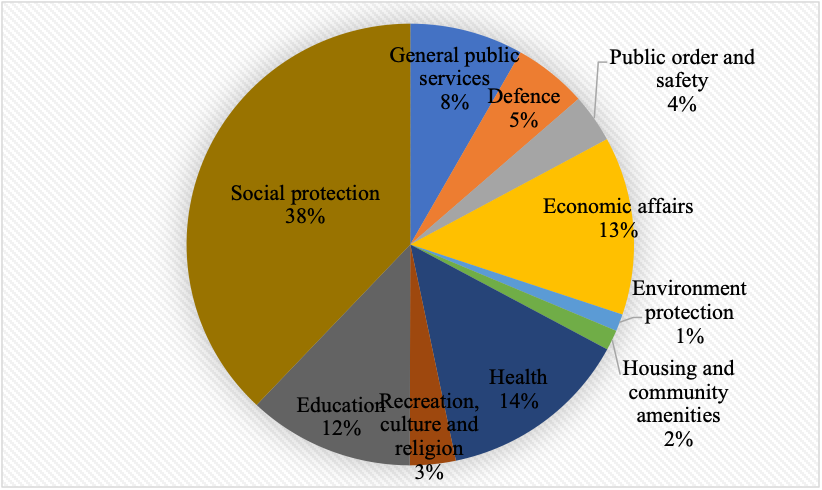
*Public expenditure on culture (ESA 2010) comprises data of the indicator CG080 “recreation, culture and religion” as it is presented in the database of Lithuanian Department of Statistics and Eurostat according to the COFOG 1999.
Over the last five years, the total public expenditure on recreation, culture and religion has been gradually increasing. Consequently, per capita cultural expenditure has also increased, both as a result of increasing appropriations for culture and population decline. The share in GDP of expenditure for culture has not changed substantially since 2015 until 2019 and was about 1 per cent of GDP. In 2020, it increased to 1.4 %.
Table 39: GDP and public expenditure on culture in 2015–2020
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| GDP at current prices, in millions EUR | 37 345 | 38 889 | 42 276 | 45 514 | 48 859 | 49 507 |
| GDP per capita at current prices, EUR | 12 884 | 13 486 | 14 796 | 16 157 | 17 486 | 17 710 |
| Public expenditure on culture (all levels), in millions EUR | 351.7 | 397.4 | 453.8 | 499.9 | 570.8 | 701.9 |
| Public expenditure on culture (all levels) in percentage of the total public expenditure in that year | 2.7 % | 3.0 % | 3.2 % | 3.2 % | 3.3 % | 3.3 % |
| Public expenditure on culture per capita, in EUR | 121 | 139 | 158 | 178 | 204 | 250 |
| Public expenditure on culture in percentage of the GDP | 0.9 % | 1.0 % | 1.1 % | 1.1 % | 1.1 % | 1.4 % |
Last update: May, 2022
Table 40. Public cultural expenditure by level of government, 2020
| Level of government | Total expenditure on recreation, culture and religion in millions EUR | Share of total pct |
| State (central) | 360.4 | 51.4 % |
| Local (municipal) | 341.5 | 48.6 % |
| TOTAL | 701.9 | 100 % |
Last update: May, 2022
There is no detailed information on the direct government expenditure on culture by sector in Lithuania. The data can only be compiled approximately according to the Annual Budget Reports of the Lithuanian Ministry of Culture, the Law on the Approval of Financial Indicators of the State Budget and Municipal Budgets for the corresponding year as well as the annual reports of the Lithuanian Council for Culture, the Film Centre, and the Press, Radio and Television Support Foundation. The data shows that the largest share of state funding is allocated to the performing arts (24.78 %). Museums come in second place (17.15 %), and libraries in third (6.29 %). Various administrative bodies, e. g. Office of the Inspector of Journalist Ethics, State Commission on the Lithuanian Language, National Commission for Cultural Heritage, as well as administration of the Lithuanian Council for Culture and Ministry of Culture itself, takes up 38 % of total funding.
Table 41: Direct state cultural expenditure by sector, 2021, in 1000 of EUR
| Field/Domain/Sub-domain | TOTAL | TOTAL |
| in 1000 EUR | in % | |
| I. Cultural Heritage | ||
| Historical Monuments | 7 965.054 | 2.48 |
| Museums | 55 117.148 | 17.15 |
| Archives | 11 350.500 | 3.53 |
| Libraries | 20 212.180 | 6.29 |
| Intangible Heritage / Folk Culture | 3 330.567 | 1.04 |
| II. Visual Arts | ||
| Fine Arts / Plastic Arts | 3 388.317 | 1.05 |
| Photography | 780.157 | 0.24 |
| Architecture*** | 709.214 | 0.22 |
| Design / Applied Arts | 464.240 | 0.14 |
| III. Performing Arts | ||
| Music | 21 111.798 | 6.57 |
| Theatre, Music Theatre, Dance | 58 398.033 | 18.17 |
| Multidisciplinary | 126.206 | 0.04 |
| IV. Books and Press | ||
| Books | 1 711.887 | 0.53 |
| Press | 1 550.170 | 0.48 |
| V. Audiovisual and Multimedia | ||
| Cinema | 7 240.509 | 2.25 |
| Television and radio | 2 139.624 | 0.67 |
| Sound recordings | - | - |
| Multimedia | 429.000 | 0.18 |
| VI. Interdisciplinary | 1 441.229 | 0.45 |
| Socio-culture | 1 723.255 | 0.54 |
| Cultural Relations Abroad | 1 158.471 | 0.36 |
| Administration | 12 1398.011 | 37.78 |
| Cultural Education | 25.000 | 0.01 |
| VII. Not covered by domain I-VI | - | - |
| TOTAL | 321 341.570 | 100% |
The Lithuanian Council for Culture provides data on the allocations of its funding by field in 2021. The Council implements two types of financing measures: funding of projects according to cultural programmes or arts fields, and funding of individual grants for artists. Data about funding are collected by the Division of Monitoring and Analysis of the Council and compiled according to the year of funding, arts fields, types of organisations, their geographical location etc.
Table 42: Allocation of funding by Lithuania Council for Culture by sector, 2021, in 1000 EUR
| Field/Domain/Sub-domain | TOTAL | of which: Transfers | ||||
| In 1000 EUR | in % | |||||
| Projects by art fields | Individual grants by field | Projects and grants together by field | Projects and grants together by field | to budgetary institutions | to NGOs, companies, individuals | |
| I. Cultural Heritage | ||||||
| Historical Monuments | 577.773 | 83.400 | 661.173 | 3.51 % | 327.266 | 333.907 |
| Museums | 1615.291 | 16.200 | 1631.491 | 8.67 % | 1 430.091 | 201.400 |
| Archives | 44.500 | 44.500 | 0.24 % | 32.500 | 12.000 | |
| Libraries | 677.975 | 9.600 | 687.575 | 3.65 % | 661.765 | 25.810 |
| Intangible Heritage / Folk Culture | 831.647 | 112.200 | 943.847 | 5.01 % | 476.404 | 467.443 |
| II. Visual Arts | ||||||
| Fine Arts / Plastic Arts | 1 069.869 | 278.400 | 1 348.269 | 7.16 % | 285.041 | 1 063.228 |
| Photography | 618.757 | 161.400 | 780.157 | 4.14 % | 167.837 | 612.320 |
| Architecture | 676.214 | 33.000 | 709.214 | 3.77 % | 26.180 | 683.034 |
| Design / Applied Arts | 307.640 | 156.600 | 464.240 | 2.47 % | 47.000 | 417.240 |
| III. Performing Arts | ||||||
| Music | 3 217.910 | 619.200 | 3 837.110 | 20.39 % | 696.180 | 3 140.931 |
| Theatre. Music Theatre. Dance | 2 316.454 | 327.000 | 2 643.454 | 14.04 % | 555.424 | 2 088.030 |
| Multidisciplinary | 1 262.060 | - | 1 262.060 | 6.71 % | 444.699 | 817.360 |
| IV. Books and Press | ||||||
| Books | 1 447.287 | 264.600 | 1 711.887 | 9.09 % | 139.650 | 1 572.237 |
| Press | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| V. Audiovisual and Multimedia | ||||||
| Cinema | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Television | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Sound recordings | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Radio | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Multimedia | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| VI. Interdisciplinary | 1 147.829 | 293.400 | 1 441.229 | 7.66 % | 308.886 | 1 132.343 |
| Socio-culture | 406.255 | - | 406.255 | 2.16 % | 110.220 | 296.035 |
| Cultural Relations Abroad | 0.000 | - | - | 0.000 | 0 | |
| Administration | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cultural Education | 250.000 | - | 250.000 | 1.33 % | 71.400 | 178.600 |
| VII. Not covered by domain I-VI | ||||||
| TOTAL | 16 467.461 | 2 355.000 | 18 822.461 | 100% | 5 780.543 | 13 041.917 |
According to the data, in 2021, the Council for Culture allocated the largest share of funding to music projects (20.39 %). Theatre projects come in second place (14.04 %), and publication and translation of literature and humanities are in third place (9.09 %). Organisations funded from state or municipal budgets got about one third of the total funding.
Last update: May, 2022
In Lithuania, several institutions provide financial support for artists and culture through funding programmes: the Ministry of Culture of the Republic of Lithuania, the Lithuanian Council for Culture, the Press, Radio, and Television Support Foundation, the Film Centre, and the Lithuanian Culture Institute.
The Ministry of Culture allocates the biggest share of state financing for culture through direct institutional funding. It also implements a range of special programmes designated to support the various fields of culture: the Reading Promotion Programme, the Lithuanian Capital of Culture Programme, Programme of Lithuanistics Traditions and Heritage, Funding Programme of Projects Implementing Initiatives to Preserve Historical Memory, several heritage protection programmes, Programme of Partial Compensation of the Cost of Dissemination (Venue Hire) of Professional Performing Arts Projects, Programme for the Partial Funding from the State Budget of Professional Performing Arts Institutions that Are not National, and the State or Municipal Theatre or Concert Institution (see chapter 3.3 for more about the last two programmes). The Ministry, in cooperation with the Lithuanian Film Centre and Lithuanian Culture Institute, also coordinates the participation of Lithuania in the EU funding programmes Creative Europe and Europe for Citizens.
Other institutions – the Lithuanian Council for Culture, the Press, Radio, and Television Support Foundation, the Film Centre, and the Lithuanian Culture Institute – implement financing programmes and allocate funding through calls for tender. Their budgets consist of appropriations allocated by the Ministry of Culture.
The Lithuanian Culture Institute implements the Translation Grant Programme. The Translation Grant Programme encourages the translation of Lithuanian literature into foreign languages and it has been operating in Lithuania since 2001. The programme was first run by the public institution “Books from Lithuania”, but since 2010 the work has been continued by the Lithuanian Culture Institute. Over the 20 years since the establishment of the programme, it has supported the translation of 461 Lithuanian literary works into 38 languages. The Press, Radio and Television Support Foundation implements 6 funding programmes: 1) periodicals of culture and art; 2) national periodical press; 3) regional periodical press; 4) national radio and television broadcasting, 5) regional radio and television broadcasting; and 6) Internet media. The Lithuanian Film Centre allocates subsidies for the development, production and distribution of Lithuanian films and international co-productions.
The Lithuanian Council for Culture implements the greatest number of funding programmes and allocates the biggest share of programme financing. The Council implements two types of financing measures: funding of projects by cultural programmes or arts fields, and funding of individual grants for artists. Financing of arts fields includes projects of architecture, circus, design, visual arts, photography, literature, music, dance, interdisciplinary arts, and theatre. Projects funded by the arts fields programme are targeted at the following activities: 1) professional creation and its dissemination in Lithuania and abroad; 2) events; 3) accumulation of information (archiving, documentation) and its dissemination; 4) publishing; 5) professional criticism and analysis; 6) networking and mobility; 7) co-production; and 8) mastery development and education. Cultural programmes financed by the Council in 2021 were the following: Memory institutions: creation of innovative services; Memory institutions: dissemination of culture and art; Memory institutions: restoration and research of cultural properties; Memory institutions: projects for the acquisition of movable cultural property important for the history of Lithuania and its culture, Ethnic culture and immaterial heritage of culture; Memory institutions: acquisition projects of contemporary visual art or design by Lithuanian artists created after 1990; Culture and creative industries: networking; Culture and creative industries: cultural start-ups; Art for human wellbeing; Protection of copyright and related rights; Creative initiatives of communities; Cultural heritage projects; Education through culture: children’s and youth culture; Periodic amateur art events; Creative community initiatives: small Lithuanian capitals of culture; Events of national importance; Publishing of humanities literature; Strategic funding of artists' organisations; Strategic funding of cultural organisations; Strategic funding of international events; and Funding of international music performance competitions organized in Lithuania.
Table 43: Budgets of the Lithuanian Council for Culture, the Press, Radio, and Television Support Foundation, the Film Centre, and the Lithuanian Culture Institute in 2021
| Institution | Allocated amount, in EUR |
| Lithuanian Council for Culture | 24 868 650 |
| Film Centre | 7 240 509 |
| Press, Radio, and Television Support Foundation | 2 736 000 |
| Lithuanian Culture Institute | 1 158 471 |
Besides Lithuanian funding programmes, artists can also apply for funding to international programmes, e.g. Nordic-Baltic mobility programme for culture: support to artists’ residencies. The Nordic-Baltic Mobility Programme for Culture aims to strengthen artistic and cultural cooperation in the Nordic region and Baltic States. The programme focuses on increasing the exchange of knowledge, contacts, presence and interest in Nordic and Baltic art and culture. The Nordic-Baltic Mobility Programme comprises three forms of funding: mobility, network and funding for artist residencies.
Last update: May, 2022
There are not many special funds in Lithuania dedicated to supporting artists of various fields. The oldest one is the Lithuanian Musicians Support Fund, established in 1992. The Fund is a public charity organisation and publishing house, which supports the development of Lithuanian musicians' creative activities, commemoration of musicians, promotion of music, and patronizes talented musicians and music veterans. The Fund implements 12 programmes, such as various concourses, festivals and education programmes.
The Lithuanian Writers Union Foundation aims to give beneficence to the members of LWU and support programmes that correspond to the aims of the Foundation or its subdivisions. In accordance with the Law on Charity and Sponsorship Funds of the Republic of Lithuania, the Literary Foundation supports the publishing of fiction, especially of an original type, management and publishing of the literary heritage of the members of LWU; literary events: conferences, literary evenings, commemoration of anniversaries, literary competitions, etc.; activities of the subdivisions of LWU, such as periodicals, publishing and bookshops; care of the memorials to writers and other remembrance programmes; and social and cultural programmes announced by Government.
The organisations of collective administration of copyright and related rights make payments for their members. National and international copyright is collectively administered by the Association LATGA established in 1991 and the Music Copyright Association NATA established in 2012. The collective administration of the performers and phonogram producers’ rights is performed by the Lithuanian Related Rights Association AGATA that was established in 1999. At the initiative of the performers and phonogram producers, the related rights association GRETA was established in 2013. The Association of Audiovisual Works Copyright AVAKA, established in 2008, administers the rights of the owners of audiovisual works. These organisations distribute royalties and make payments to represented right holders.
AVAKA has a Sociocultural Fund that is used to strengthen the audiovisual sector and encourage creativity through support of events, concourses, festivals, workshops, conferences and other activities, which enhance the professional competences of TV and film producers. The fund also can be used for special payments to AVAKA members in case of accidents, illness or death.
Last update: May, 2022
The main institution allocating grants for Lithuanian artists is the Lithuanian Council for Culture. The Council awards two kinds of grants: individual and educational grants. Individual grants are awarded to support individual artistic activities of culture or art creators in the amount of 600 EUR per month and may be awarded for a maximum of 2 years. Education grants are awarded for improving the professional skills of culture or art creators, in particular for participating in traineeship programmes, courses, conferences, symposiums and other activities for building up professional skills. Education grants may also be used for covering the costs of creative residencies or master classes. The grants amount to 3 600 EUR and may be awarded for a maximum of 6 months.
Table 44: Individual grants for artists by field of arts, distributed by the Lithuanian Council of Culture in 2014–2022
| Forms of art | Number of grants distributed | Amount allocated in EUR |
| Circus | 82 | 164 747 |
| Architecture | 126 | 276 191 |
| Museums | 143 | 210 470 |
| Film | 106 | 253 421 |
| Libraries | 174 | 244 995 |
| Traditional Arts | 272 | 621 344 |
| Dance | 293 | 598 965 |
| Cultural Heritage | 290 | 676 225 |
| Design | 344 | 876 783 |
| Photography | 294 | 879 435 |
| Literature | 695 | 1 993 430 |
| Theatre | 809 | 1 615 887 |
| Interdisciplinary Arts | 668 | 1 892 549 |
| Visual Arts | 1 048 | 2 843 276 |
| Music | 1 372 | 3 070 697 |
| Total | 6 716 | 16 218 415 |
The Ministry of Culture of the Republic of Lithuania gives annual awards and prizes for outstanding achievements in arts and culture. The most important award is the Lithuanian National Award for Culture and Arts. The award was established in 1989. It is granted for outstanding achievements in culture and arts and has been awarded annually in six categories since 2006 (between 1989 and 2006 there were nine categories). The prize is formally bestowed on February 16, when the decorations and diplomas are presented to the laureates at the Presidential Palace, commemorating the anniversary of the 1918 Act of Independence of Lithuania.
The Lithuanian Government Awards for Culture and Arts were established in 2006 and aim to promote art creators, performers, musicians, film makers etc. for their merits to Lithuanian art. Up to 12 awards are granted by the Lithuanian Government annually to Lithuanian cultural and artistic creators and actors.
The most significant works of professional theatre creators and outstanding professional achievements in the fields of drama, opera, operetta and musical, ballet, dance, puppet and object theatre, as well as children’s and youth theatre, are awarded with prizes conferred by the Ministry of Culture – the Golden Stage Cross and the Borisas Dauguvietis Earring. The award ceremony is held on World Theatre Day – 27 March.
In order to encourage and appreciate the creators, translators and critics of literature, the Ministry of Culture has been annually awarding premiums for the best works: the Armchair of the Translator of the Year (in cooperation with the Lithuanian PEN Centre), St. Jerome’s Prize (in cooperation with the Lithuanian Association of Literary Translators), as well as the Yotvingian Prize and the Young Yotvingian Prize (in cooperation with the Association “Druskininkai Poetic Fall”).
The Ministry of Culture organises the Dalia Tamulevičiūtė Competition for Lithuanian Authors of Performing Works of Art – a winner is selected from the sketches/extracts of performing works of art submitted to the Ministry of Culture from professional performing arts theatres according to the established procedure, to whom funding is allocated for the production of a play or one-person play.
The Balys Buračas photography award is annually granted to Lithuanian photographers for the most significant work or series of works that analyse, document or interpret Lithuanian culture.
The Bronius Savukynas award was established in 2010 by the Ministry of Culture. The award is granted annually to authors of publications and chief editors of cultural publications for the purity and correctness of the Lithuanian language, and the dissemination of humanistic values, analytical thought, and intellectual culture in periodical cultural publications.
The Young Artist Prize is awarded annually by the Ministry of Culture. Nominees for the prize may be either young artists (14 to 35 years old) or teams of young artists.
The Martynas Mažvydas Premium for merits to the Lithuanian language, history of writing and book art is awarded for the best research achievements in Lithuanian literature, language history, culture, and book science.
Last update: May, 2022
There are 19 artists’ associations in Lithuania that have a special status of “artists’ organisation” granted them according to the Law on the Status of Artists and Artists Organisations (1996): Architects’ Association of Lithuania, Lithuanian Union of Journalists, Lithuanian Theatre Union, Professional Folk Artists’ Association, Lithuanian Writers’ Union, Lithuanian Musicians’ Union, The Lithuanian Association of Literary Translators, Lithuanian Composers’ Union, Lithuanian Filmmakers’ Union, Union of Lithuanian Art Photographers, Lithuanian Designers’ Society, Lithuanian Artists’ Association, Lithuanian Association of Landscape Architects, Contemporary Dance Association, Lithuanian Interdisciplinary Artists’ Association, Association of Performing Arts Critics, Lithuanian Association of Chores, Association of Vilnius Region Folk Artists, Lithuanian Association of Art Creators. The latter organisation is an umbrella association of twelve artists unions.
Artists' unions and associations that have the status of “artists’ organisations” can apply for funding to the special programme “Strategic Programmes of Artists Organisations”, created by the Lithuanian Council for Culture to support these kinds of organisations. In 2021, the programme funded 18 projects of these organisations in the amount of 1 250 000 EUR.
Last update: May, 2022
Private funding for culture is regulated in by the Law on Charity and Sponsorship (1993), the Law on Patronage (2018),the Law on Personal Income Tax (2002) and the Law on Corporate Income Tax (2001) (see chapter 4.1.4).
Data about the sponsorship provided and received by legal persons are collected by the Lithuanian Department of Statistics. According to this data, legal persons working in the fields of creative, arts and entertainment activities, libraries, archives, and museums received more than 4 million EUR sponsorship in 2020. Compared to other areas, these activities receive three times less support than education, and almost 8 times less than sport, amusement and recreation activities. The total amount provided by sponsors for culture did not change significantly over the last five years.
Table 45: Support received by legal persons in various fields in 2015–2020 (in EUR thousand)
| Field | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Creative, arts and entertainment activities Libraries, archives, museums and other cultural activities | 4 768.9 | 4 316.3 | 4 908 | 5 179.7 | 4 407.3 | 4 049.1 |
| Education | 11 481.8 | 14 813.9 | 12 325.4 | 13 930.6 | 15 451.9 | 13 784.0 |
| Sports, amusement and recreation activities | 31 867.4 | 34 226.7 | 31 520.0 | 35 001.6 | 38 399.0 | 29 515.7 |
According to Article 34 of the Law on Personal Income Tax, after the end of the tax period, the tax administrator must, at the request of a resident of Lithuania and in accordance with the procedure established by the Government, transfer to Lithuanian entities that are entitled to sponsorship under the Law on Charity and Sponsorship an amount not exceeding 1.2 % of the income tax payable on the basis of an annual income tax return. According to the data of the Lithuanian State Tax Inspectorate, in 2019, at the requests of the residents of Lithuania, the inspectorate transferred a total of 21 096 378 EUR to 23 492 organisations entitled to receive sponsorship. However, the data on how much of this of sponsorship went to artists and cultural organisations is not available.
The amendment to the Law on Corporate Income Tax in 2013 stimulated the private funding of Lithuanian cinema. Article 172 of the Law states that in calculating corporate income tax, funds granted free of charge to a Lithuanian filmmaker for the production of a film or a part thereof in the Republic of Lithuania may be deducted from taxable income (more about the Law see chapter 4.1.4). According to the information of the Lithuanian Film Centre, the Film Tax Incentive is increasing each year. In 2021, filmmakers received more than 15 mln Euro of gratuitous investments by taking advantage of the Incentive. Compared with the results of 2020 the sum of financial aid has grown by 26%. That is the highest sum received through the whole period since 2014, when the Incentive was started. By taking advantage of the Incentive, international filmmakers have spent as much as 37.9 mln Euro and have surpassed the spending of the previous years significantly. The number of financed films has grown as well. A total of 71 new films that took advantage of the Incentive were financed in 2021, of those – 40 were domestic, 19 foreign productions and 12 co-production film projects.
The Law on Patronage, adopted by the Seimas in 2018, has not yet made a significant impact on private funding for culture. The Law provides that the title of a national patron is awarded to a person who has provided at least one million EUR in support to the patronage project(s) at the state or more than one municipality level. A title of patron of a municipality is awarded to the person who has provided at least 150 000 EUR in support of a patronage project(s) in the municipality with a permanent population of 25 000 or less, and in the case of the municipalities with more than 25 000 permanent residents, the title of a municipal patron is awarded to a person who has provided at least 250 000 EUR support for the implementation of sponsored project(s) at municipal level. The Government assesses the compliance of the projects with the requirements of this Law, recognises the projects as appropriate to patronage, grants the title of the national patron and adopts decisions on the loss of the title of national patron on the proposal of the Patronage Council. In 2018, the Patronage Council awarded the first title of national patron for the one million EUR support for the Balbieriškis Church restoration project. During the 2019, 2020 and 2021 the Patronage Council awarded the titles of the patrons of municipality to 9 persons and enterprises.
